Sign In
Welcome to Bypass AI! Sign in to continue your exploration of our platform with all its exciting features.
Forgot Password?
Don’t have an account ? Sign up
Sign Up
Embrace the Future with Bypass AI! Sign up now and let's rewrite the possibilities together.
You have an account ? Sign In
Enter OTP
We’ll send you an OTP on your registered email address
Back to Login
Forgot Password
We'll Send You An Email To Reset Your Password.
Back to Login
Enter OTP
We'll send you an email to reset your password.
Back to Login
Confirm Password
Please enter your new password.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Quick Summary
What Is Plagiarism, And Why Should It Be Avoided?
Different Types of Plagiarism
Conclusion
FAQs
The world has changed with the free flow and simple access to information, making writing easier but also more challenging. Generally, the availability of information aids in a person's store of knowledge, but it also exposes a person to plagiarism, either intentionally or accidentally. This is the presentation of someone else's work, ideas, or intellectual property as your own without proper acknowledgement. Plagiarism is considered a violation in matters of ethics and education and can be more serious, leading to reputational damage, legal issues, or even potential reductions in academia.
With this understanding of the different types of plagiarism, the task of avoiding them is made easy for any writer, student, or professional. The seven most common types of plagiarism, their meanings, and how avoiding them is important will be discussed.
Quick Summary
Plagiarism is not only the copying of some texts word to word but is present in different forms, some of which might even be unintentional. Therefore, this guide will explain in detail the seven most common forms of plagiarism that may help a person know them, avoid plagiarism and retain the value of originality through his writing.
What Is Plagiarism, And Why Should It Be Avoided?
Plagiarism is the crime of intellectual honesty. It occurs when one man uses the work of another man without giving credit to the respective owner. This may occur in various situations, like in an academic field, while creating content, in journalism, or a professional setup. These are some of the reasons why there should be no plagiarism:
Ethical Integrity: Plagiarism is theft because one steals credits meant for the work done by someone else. It violates other people's rights to intellectual property. It denies justice that the problem with the idea they stole comes to haunt them.
Academic and Professional Implications: In educational settings, it may result in failing grades, suspension, and expulsion. In the professional world, it may translate to job loss and legal action or loss of credibility.
Lack of Learning and Intellectual Development: Another negative outcome of plagiarism, copying others' work, is that one fails to learn and intellectually develop. The process of producing the original content helps in developing the ability for critical thinking, creativity, and solving problems.
Different Types of Plagiarism
Plagiarism can take many forms. Some are very obvious: a person copies and pastes words, for example. Others can be less obvious, such as when a person paraphrased inaccurately. Here are the seven common kinds of plagiarism:
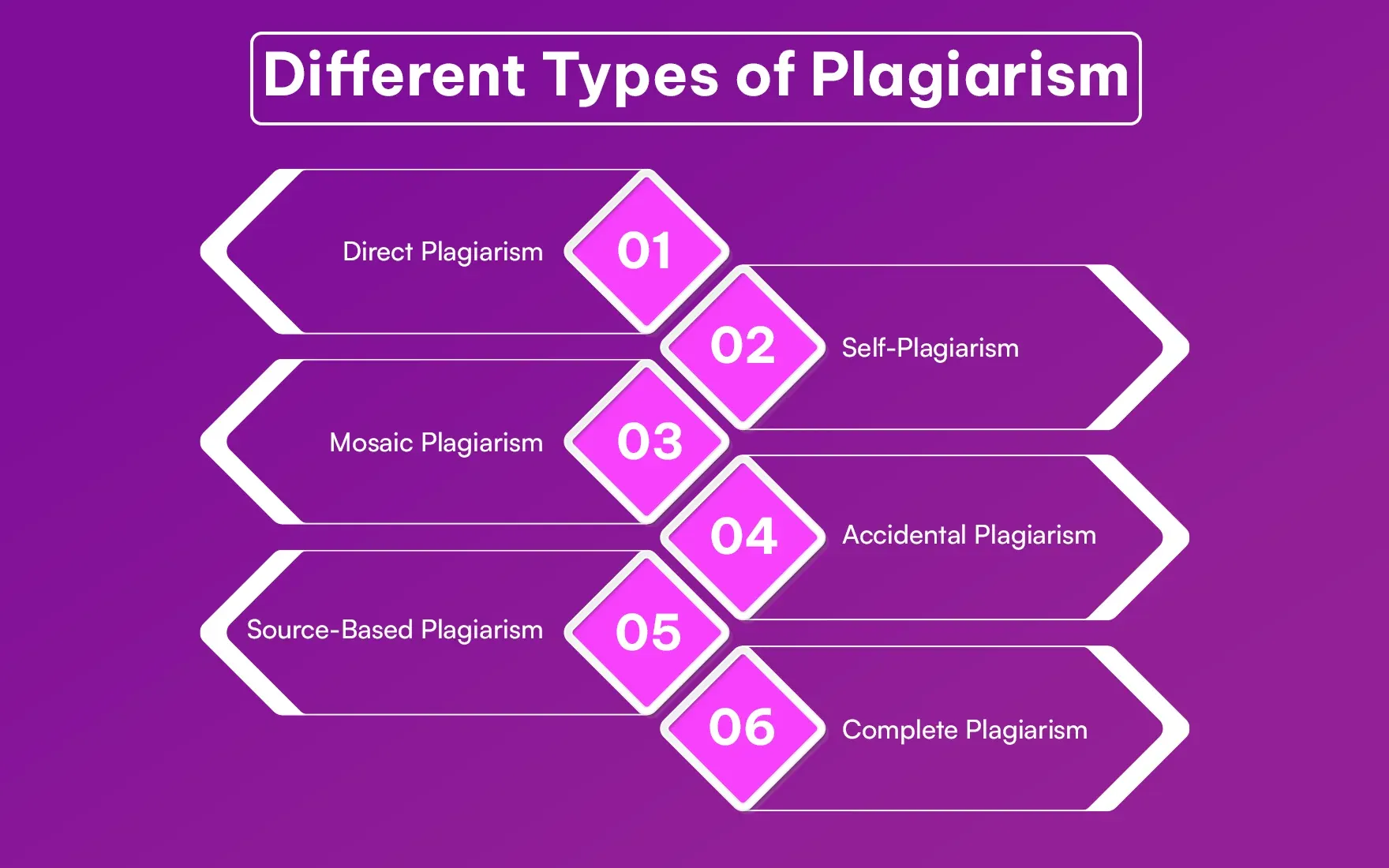
1. Direct Plagiarism
Definition: Direct plagiarism refers to the process where an individual copies a portion of someone's work into their own without giving full reference. This is the most overt form of plagiarism, and hence black-and-white. Typically, this involves total copying of an entire section of content in a word-to-word manner and no effort of paraphrasing or summarizing.
Example: Copying an entire paragraph from an article on the Internet pastes it into a research paper without quotation marks or citations.
Why It Should Be Avoided: Direct plagiarism is presenting another's work as your own to be done with the deliberate intent. This is not in line with any ethical codes of any particular discipline that you are or may be involved in and can even result in some very severe academia-related or professional consequences.
Solution: To avoid direct plagiarism, always enclose the word within quotation marks when copying word for word and properly cite from where you obtained it. Try to paraphrase and give credit to the original author whenever possible.
2. Self-Plagiarism
Definition: Self-plagiarism is the use of one's own published or submitted work without permission or acknowledgement. It is a little less objectionable than plagiarism, but it still misleads the reader that the material is a new one.
Example: Submitting the same research paper for two different classes without seeking prior permission from the instructors.
Why Avoid It: Self-plagiarism weakens the aspect of academic integrity, thus making readers confuse you for having come up with new content while re-printing your old material. Additionally, if such material already exists in another published form, then you might be violating the copyright agreement.
Solution: Always reveal whether you are borrowing parts of a piece from an earlier work. Apply, if necessary, for permission to reprint previously published work by professors or publishers.
Also read this article: 12 Plagiarism Checker Tools
3. Mosaic Plagiarism
Definition: This is also termed patchwriting, where the writer blends phrases, ideas, or text from various sources to form a new work without adequately referencing the sources. In this technique, the writer changes some words or makes inconsiderable modifications to the original construction, but still, they do not give proper credit to the original source.
Example: Collecting some sentences from different sources, making some minor changes in wording and then presenting them as your own work.
Why Avoid It: Mosaic plagiarism is sneaky because it has a flavour and semblance of being an original piece, but it usually draws on the intellectual property of someone else. It's trickier to spot, but it's no less dishonest.
Solution: Avoid Mosaic Plagiarism. Paraphrase thoroughly, and always cite your sources. Redraft the idea in your own words instead of just changing some words here and there. Properly attribute it.
4. Accidental Plagiarism
Definition: plagiarism whereby an individual unconsciously does not use proper citation rules or inadvertently paraphrases too closely to the original text. It usually occurs due to a lack of knowledge of citation rules or inaccuracy in tracking sources during research.
Example: Forgetting to place a source on a list of works cited or paraphrasing a sentence so closely that it is very much like the original text.
Why It Should Be Avoided: Although accidental plagiarism is not performed with bad intentions, a grave penalty can be expected, for example, academic sanctions. The fact that the work is plagiarized makes no difference with regard to intent.
Solution: Proper notes should be taken while researching and watching every source. Also, all the direct quotes, paraphrases, and ideas of others will be appropriately cited. One should rely on plagiarism detection tools also while cross-checking one's work.
5. Source-Based Plagiarism
Definition: This is when source-based plagiarism is characterized by misrepresenting or altering sources. It may be in the form of incorrect citations, nonexistent source citations, and failure to acknowledge the work of a previous author. It also happens if an author cites from a second-hand resource as if he or she has consulted the original source directly.
Example: Quoting a source that was referenced in another paper but did not refer to the actual material.
Why It Should Be Avoided: This form of plagiarism warps the very fabric of academic rigour and, therefore, also misleads readers about the quality of your research. It also undermines the work of the original authors.
Solution: Always check sources you cite and make sure that you actually cite them. When using secondary sources, indicate what it is that you are using: a secondary reference, rather than claiming access to primary sources.
6. Complete Plagiarism
Definition: Integral plagiarism is the taking or buying of an entire work and submitting it as one's own. This is the most extreme form of plagiarism, including submitting someone else's research paper, essay, or article as one's own work.
Example: A student buys a prewritten paper off the Internet and submits it at the completion of an assignment.
Why It Should Be Avoided: Completely plagiarized work is academic fraud, and it will get you expelled, sue someone against you, or even cost you your reputation on permanent grounds. That is a simple and gross violation of ethical codes of conduct and a complete denial of respect for intellectual integrity.
Solution: Always produce original work and cite sources that have inspired your research or writing work. Never submit work from another person as your own work.
Conclusion
Plagiarism in any form corrupts work integrity and can provoke grave consequences. Direct copying, poor paraphrasing, or failure to properly account for sources, thereby amounting to a lack of respect for intellectual property, plagiarism reflects a lack of respect for intellectual property. Knowledge of different types of plagiarism helps avoid these errors and ensures that work is original and ethical.
With Bypass plagiarism checker, there can be total assurance in perfect plagiarism detection to ensure content originality with a more subtle advancement in the algorithms that can even detect the faintest traces of plagiarism. Therefore, writers will enjoy high-quality and integrity work with this tool.
FAQs
1. What is plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the use of someone else’s work, ideas, or intellectual property without proper citation.
2. Why is plagiarism unethical?
It violates the intellectual property rights of others, breaches academic integrity, and results in reputational, academic, or legal consequences.
3. What are some common types of plagiarism?
Common types are direct plagiarism, self-plagiarism, mosaic plagiarism, accidental plagiarism and source-based plagiarism as well as complete plagiarism.
4. How can plagiarism be avoided?
Plagiarism can be avoided by proper citation of sources, accurate paraphrasing, meticulous note-taking during research, and the use of plagiarism detection software.
5. What is the penalty for plagiarism?
Penalties can include anything from failing grades and academic suspension to legal consequences, loss of employment, or permanent damage to one's reputation.




